NEPHROLOGY and HYPERTENSION

Dr D’Souza is also associated with the renowned Hypertension Unit at Greenslopes Private Hospital and manages patients with resistant hypertension with a focus on primary hyperaldosteronism and renovascular hypertension.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is defined as a gradual loss of kidney function over 3 or more months. CKD is divided into stages 1- 5. Patients with protein in the urine and poor blood pressure control are at a higher risk of progressing to end stage renal failure. Early intervention is crucial in preventing progressive renal dysfunction.
A low haemoglobin (anaemia) is common in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 3-5. This occurs as a result of erythropoietin deficiency. Reversible conditions such as iron , B12 and folate deficiency should be corrected in the initial instance. Patients may require an erythropoietin stimulating agent (which is an injection) given at variable frequency to address the anaemia.
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) is an abrupt or sudden deterioration in kidney function associated with a rise in serum creatinine and a reduction in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Patients symptoms can range from being asymptomatic to presenting with a reduction in urine output, increasing confusion, nausea and vomiting as well as feeling tired. There are various different causes for an acute kidney injury which can be delineated via blood , urine tests and an ultrasound of the kidneys.
Dialysis or renal replacement therapy is inevitable in symptomatic patients with end stage renal failure due to the accumulation of uraemic toxins and issues with fluid balance. There are various different dialysis modalities including peritoneal dialysis, home haemodialysis and in centre haemodialysis. A referral to a surgeon for access formation for dialysis (Arteriovenous fistula or a peritoneal dialysis cathether) will need to be organized prior to initiation of renal replacement therapy.
Resistant hypertension is defined as a persistent blood pressure of >140/90 despite lifestyle modification and 3 antihypertensive agents including a diuretic. It is essential to investigate and exclude secondary causes in patients with resistant hypertension. Secondary causes include conditions such as primary aldosteronism or Conn’s syndrome, renal artery stenosis, pheochromocytoma and cushings syndrome. Optimization of blood pressure is crucial in preventing target end organ damage.
Kidney transplantation should be considered for suitable patients with end stage renal failure and dialysis dependency as it improves survival and quality of life. This includes living donor and deceased donor renal transplantation. Various blood tests, cardiac investigations and imaging will need to be performed prior to a referral to the local transplant unit for a transplant assessment.
CONSULTING AT MULTIPLE LOCATIONS
Level 3 – Suite 301, 6 North Lakes Drive, North Lakes QLD 4509
07 3193 0875
Fax: 07 3319 6653
reception@drroshini.com.au
Po Box 242
Aspley,
QLD 4034
This is an article that Dr Roshini wrote for ‘acute matters which was a HSN newsletter that goes out to GP’s’ which talks about CKD(chronic kidney disease). Read part of the article and download it in full as PDF file.
Worldwide, CKD is a recognised health burden with increasing number of patients commencing renal replacement therapy (RRT). CKD leads to significant morbidity and mortality with a large contribution from cardiovascular complications. Early detection of CKD is the key in preventing progression of renal impairment and attendant comorbidities.
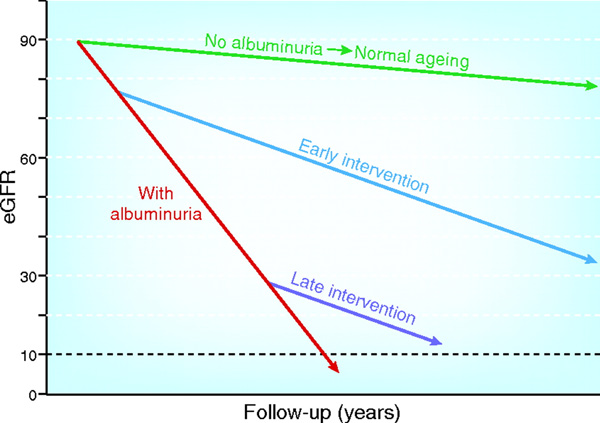
CKD is defined as abnormalities of kidney structure or function reflected by a glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of <60ml/min/1.73 m2 for 3 months 1. Microalbuminuria has been incorporated into the staging of CKD to stratify individuals at added risk of progression to End Stage Renal Failure (ESRF) ie a GFR <15 ml/min/1.73m2. Early intervention to reduce albuminuria prevents a rapid decline in eGFR shown in Figure 12.
Dr D’Souza is dedicated to providing a renal consulting service within the hospital.
She strives to achieve the best outcomes for her patients with a focus on evidence based medicine.